Canonical message service technical reference
The message service is responsible for cross-chain messages between Ethereum and Linea, which:
- Allows a contract on the source layer to safely interact with a contract on the target layer (e.g. L1TokenBridge triggering mint on the L2TokenBridge),
- Is responsible for bridging ETH (native currency on L1 and L2)
- Supports:
- push: auto-execution on target layer if a fee is paid
- pull: users/protocols responsible for triggering the transaction
Contracts
- Mainnet
- Linea Sepolia
| L1 (Ethereum) Address | L2 (Linea) Address |
|---|---|
0xd19d4B5d358258f05D7B411E21A1460D11B0876F | 0x508Ca82Df566dCD1B0DE8296e70a96332cD644ec |
| L1 (Sepolia) Address | L2 (Linea Sepolia) Address |
|---|---|
0xB218f8A4Bc926cF1cA7b3423c154a0D627Bdb7E5 | 0x971e727e956690b9957be6d51Ec16E73AcAC83A7 |
Usage
Step 1: Send a message
Call sendMessage() on the origin layer using the proxy contract at one of the contract addresses
above.
Proxy contract?
A proxy contract is one that simply points towards the actual "implementation" contracts. This model is beneficial as it allows the implementation contracts to be upgraded independently of the proxy, allowing contract upgrades without having to start afresh and lose the proxy contract's history. When the implementation contracts are updated, the proxy contract is simply amended to point towards the new implementation contract addresses.
sendMessage() takes the following arguments:
_to: the destination address on the destination layer_fee: the message service fee on the origin layer.- An optional field used to incentivize a postman to perform
claimMessage(...)automatically on the destination layer (not available when bridging from L2 to L1, or for non-ETH transfers)
- An optional field used to incentivize a postman to perform
_calldata: a flexible field that is generally created usingabi.encode(...)
What is the _fee?
L1 -> L2:
- Automatic claiming: 0 (The postman fee is sponsored by Linea.)
- Manual claiming: 0
The postman fee for automatic claiming is only sponsored for transactions using less than
250,000 gas. Where sponsorship doesn't apply, the postman fee = target layer gas price * (gas estimated + gas limit surplus) * margin, where:
target layer gas price=eth_gasPriceon the target layergas estimated= the current gas estimationgas limit surplus= 6000margin= 2
L2 -> L1:
- Manual claiming: 0.001 ETH (anti-DDOS fee)
Automatic claiming is not available for L2 -> L1.
See our main bridge page for more information on the execution fees that apply.
Step 2: Claim a message
Once the message is sent, you must execute the message on the destination layer by claiming it.
Option 1: Run a postman
You can run a postman locally or as part of a dapp to claim messages. This can be useful if messages don't get picked up by the Linea postman because there was no fee attached or the fee was too low, for example. Event filtering, detailed below, also makes it possible to filter for messages that relate to specific criteria, such as messages sent on a specific dapp.
Run a postman by cloning the Linea monorepo locally and following the instructions in the postman README.
You can trigger a manual claim via the postman by:
-
Event filtering: Run the postman with event filtering configuration that instructs it to listen only for messages that meet certain criteria. Configure the event filtering in your local
.envfile (available asenv.samplewhen you clone the monorepo):L1_EVENT_FILTER_FROM_ADDRESS: Filter events using afromaddressL1_EVENT_FILTER_TO_ADDRESS: Filter events using atoaddressL1_EVENT_FILTER_CALLDATA: Filter by the contents of event calldata using a Filtrex expression. For example:calldata.funcSignature == "0x6463fb2a" and calldata.params.messageNumber == 85804L1_EVENT_FILTER_CALLDATA_FUNCTION_INTERFACE: Filter by the calldata data function interface, following this format:"function transfer(address to, uint256 amount)". Make sure you specify parameter names in order, using syntax likecalldata.params.messageNumber.
-
claimMessage: This call is made automatically by the postman if the configuration is correct. If, however, gas exceeds 250,000 (the threshold for postman fee sponsorship), you will need to call one of these methods using the parameters detailed in the interface below:- L2:
claimMessage - L1:
claimMessageWithProof
- L2:
Option 2: Use the Linea SDK
The Linea SDK (view the npm package) simplifies the execution of messages on the destination layer.
Install the SDK using the package manager of your choice. For example:
npm install @consensys/linea-sdk
Refer to the SDK README for directions on initializing the SDK and enabling read-write mode.
Now you can use the claim() function on the destination layer to claim messages, passing the
message hash as an argument:
const tx = await l2Contract.claim(message);
You can call claim() either on the l1Contract or l2Contract depending on which you need.
Claim old messages
The Linea native bridge app only retains unclaimed message for 90 days; if your bridge transfer is older than this, you'll need to claim it outside of the native bridge app using a block explorer or the Linea SDK. We recommend you use the SDK, particularly if you're claiming on L1.
Since the message service fee is automatically set to 0 for all deposits to Linea (L1 -> L2) using less than 250,000 gas, your transaction will be claimed by the postman service automatically in most cases.
Select the appropriate message service contract for your destination layer:
- L1 (Ethereum):
- L2 (Linea):
On the contract's page, find the "Contract" tab and then select the "Write as proxy" tab:
Make sure your wallet is connected using the "Connect to Web3" button immediately above contract functions.
The function you need to use to claim your funds depends on the layer you're claiming on:
- L1 -> L2: use
claimMessage - L2 -> L1: use
claimMessageWithProof
If your L2 -> L1 transfer predates the L2 block 2242568 (Alpha v2, early 2024), use
claimMessage rather than claimMessageWithProof. See the release notes
for more information.
- L1 -> L2
- L2 -> L1
Click the claimMessage function to see its parameters. You'll need to fill these out to claim
your bridged funds:
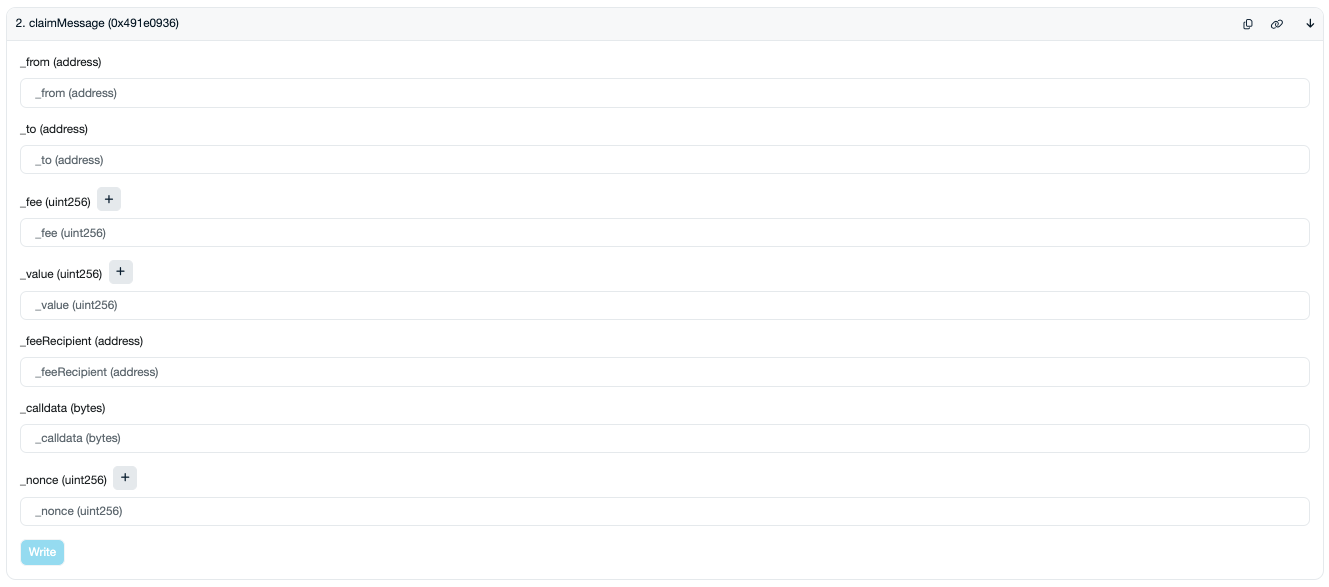
_from: The address that sent the transfer on L1._to: The recipient address on the destination layer._fee:0._value: The amount of ETH to claim, in wei._feeRecipient:0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000_calldata: Leave blank._nonce: The next nonce in sequence on the account you're using to claim. To find it, find the account's latest transaction on Lineascan. Click to open it, and then find the nonce listed under "Other attributes".
In most cases, the _from and _to address will be identical, unless you intentionally
specified a different recipient when bridging.
When ready, click the "Write" button underneath the parameters to prompt the transaction in your wallet, and then confirm it to execute the claim.
We don't recommend manually claiming messages on L1 with claimMessageWithProof, as gathering
the parameters is complex and involves querying for various events to reconstruct the proof.
Instead, we recommend using the Linea SDK, which abstracts away most of this complexity. See the SDK documentation for guidance on claiming on L1.
Interface IMessageService.sol
IMessageService.sol
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
interface IMessageService {
/**
* @dev Emitted when a message is sent.
* @dev We include the message hash to save hashing costs on the rollup.
*/
event MessageSent(
address indexed _from,
address indexed _to,
uint256 _fee,
uint256 _value,
uint256 _nonce,
bytes _calldata,
bytes32 indexed _messageHash
);
/**
* @dev Emitted when a message is claimed.
*/
event MessageClaimed(bytes32 indexed _messageHash);
/**
* @dev Thrown when fees are lower than the minimum fee.
*/
error FeeTooLow();
/**
* @dev Thrown when fees are lower than value.
*/
error ValueShouldBeGreaterThanFee();
/**
* @dev Thrown when the value sent is less than the fee.
* @dev Value to forward on is msg.value - _fee.
*/
error ValueSentTooLow();
/**
* @dev Thrown when the destination address reverts.
*/
error MessageSendingFailed(address destination);
/**
* @dev Thrown when the destination address reverts.
*/
error FeePaymentFailed(address recipient);
/**
* @notice Sends a message for transporting from the given chain.
* @dev This function should be called with a msg.value = _value + _fee. The fee will be paid on the destination chain.
* @param _to The destination address on the destination chain.
* @param _fee The message service fee on the origin chain.
* @param _calldata The calldata used by the destination message service to call the destination contract.
*/
function sendMessage(address _to, uint256 _fee, bytes calldata _calldata) external payable;
/**
* @notice Deliver a message to the destination chain.
* @notice Is called automatically by the Postman, dApp or end user.
* @param _from The msg.sender calling the origin message service.
* @param _to The destination address on the destination chain.
* @param _value The value to be transferred to the destination address.
* @param _fee The message service fee on the origin chain.
* @param _feeRecipient Address that will receive the fees.
* @param _calldata The calldata used by the destination message service to call/forward to the destination contract.
* @param _nonce Unique message number.
*/
function claimMessage(
address _from,
address _to,
uint256 _fee,
uint256 _value,
address payable _feeRecipient,
bytes calldata _calldata,
uint256 _nonce
) external;
/**
* @notice Returns the original sender of the message on the origin layer.
* @return The original sender of the message on the origin layer.
*/
function sender() external view returns (address);
}
Abstract contract MessageServiceBase.sol
MessageServiceBase.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: OWNED BY Consensys Software Inc.
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import "./interfaces/IMessageService.sol";
/**
* @title Base contract to manage cross-chain messaging.
* @author Consensys Software Inc.
*/
abstract contract MessageServiceBase {
IMessageService public messageService;
address public remoteSender;
uint256[10] private __base_gap;
/**
* @dev Thrown when the caller address is not the message service address
*/
error CallerIsNotMessageService();
/**
* @dev Thrown when remote sender address is not authorized.
*/
error SenderNotAuthorized();
/**
* @dev Thrown when an address is the default zero address.
*/
error ZeroAddressNotAllowed();
/**
* @dev Modifier to make sure the caller is the known message service.
*
* Requirements:
*
* - The msg.sender must be the message service.
*/
modifier onlyMessagingService() {
if (msg.sender != address(messageService)) {
revert CallerIsNotMessageService();
}
_;
}
/**
* @dev Modifier to make sure the original sender is allowed.
*
* Requirements:
*
* - The original message sender via the message service must be a known sender.
*/
modifier onlyAuthorizedRemoteSender() {
if (messageService.sender() != remoteSender) {
revert SenderNotAuthorized();
}
_;
}
/**
* @notice Initializes the message service and remote sender address
* @dev Must be initialized in the initialize function of the main contract or constructor
* @param _messageService The message service address, cannot be empty.
* @param _remoteSender The authorized remote sender address, cannot be empty.
**/
function _init_MessageServiceBase(address _messageService, address _remoteSender) internal {
if (_messageService == address(0)) {
revert ZeroAddressNotAllowed();
}
if (_remoteSender == address(0)) {
revert ZeroAddressNotAllowed();
}
messageService = IMessageService(_messageService);
remoteSender = _remoteSender;
}
}